What are the Different Types of Cancer?

Cancer is a complex and diverse group of diseases characterized by the abnormal growth of cells. It can affect any part of the body and can manifest in various forms. Understanding the different types of cancer is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention efforts. In this blog, we will explore the various categories and types of cancer
Cancer can be classified into more than 200 different types based on their origin in the body, such as breast cancer and lung cancer, as well as the type of cell in which they originate. Five main groups can be classified based on their cellular development. These classifications provide essential insights into the nature and behavior of various cancers, aiding in diagnosis, treatment, and research efforts. There are five main types of cancer. They are
Carcinoma
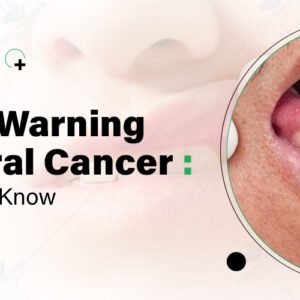
Carcinoma is the most common type of cancer, originating in the epithelial cells that cover the body’s surfaces and line the internal organs. Different types of epithelial cells can develop into various forms of carcinoma, including:
Squamous cell carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Transitional cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma
This category includes cancers such as:
Breast Cancer: Affects the breast tissue and is one of the most prevalent cancers among women worldwide.
Lung Cancer: Develops in the lungs and is associated with various factors, including exposure to environmental pollutants and genetic predisposition.
Prostate Cancer: Occurs in the prostate gland of men and is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in men.
Sarcoma
Sarcoma arise in the body’s connective tissues, including bones, muscles, cartilage, and blood vessels. These make up less than 1% of every 100 cancers diagnosed every year. Examples of sarcomas include:
Osteosarcoma: A type of bone cancer that usually develops in the long bones of the arms and legs, often affecting children and young adults.
Soft Tissue Sarcoma: Can develop in muscles, fat, nerves, tendons, and blood vessels, and can occur anywhere in the body.
Leukemia
Leukemia are cancers that affect the blood cells and bone marrow, disrupting the normal production and function of white blood cells. They are among the most prevalent types of cancer diagnosed in children and adults. Main classifications include:
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): ALL is the most common type of leukemia in children, representing about 25% of all childhood cancers. It originates from early forms of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell crucial for the immune system.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): CLL is more commonly diagnosed in older adults, particularly those over 60 years of age. Unlike ALL, CLL progresses slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages. CLL originates from abnormal lymphocytes in the bone marrow and blood.
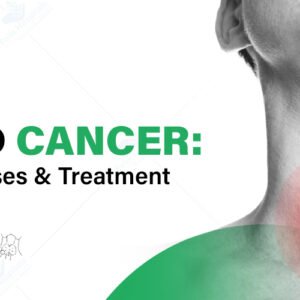
Lymphoma
Lymphoma affects the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system. It happens because some of the lymphatic system’s white blood cells (lymphocytes) start to divide abnormally and don’t die as they should. The lymphatic system includes the lymph nodes (lymph glands), spleen, thymus gland, and bone marrow. Lymphoma can affect all those areas as well as other organs in the body. Two main types of Lymphoma are
Hodgkin Lymphoma: Hodgkin lymphoma usually starts in the lymph nodes and can spread to other organs.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: This category includes a diverse group of lymphomas that originate from white blood cells called lymphocytes, with various subtypes and characteristics. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma are among the most common subtypes
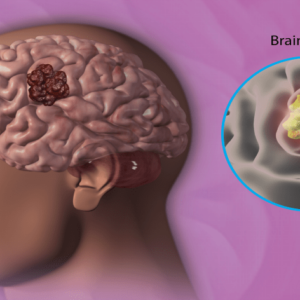
Central Nervous System (CNS) Cancer
CNS cancer affects the brain and spinal cord and can be benign or malignant. Types of CNS cancers include
Gliomas: These arise from glial cells in the brain and can be either aggressive or slow-growing
Meningiomas: These develop in the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, and are usually benign. This is the most common type of cancer that develops in the head.
Other types of cancer
In addition to the five main types of cancer listed above, there are many other types of cancer, including
Melanoma: This type of cancer starts in the melanocytes, which are the cells that produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Melanoma is a relatively rare type of cancer, but it can be very aggressive.
Germ cell cancer: This type of cancer starts in the cells in the reproductive organs. Germ cell cancer is most common in young adults.
Neuroendocrine cancer: This type of cancer starts in the neuroendocrine cells, which have both neuronal and endocrine properties. Neuroendocrine cancers can occur in many parts of the body, including the lungs, stomach, and pancreas.
Prevention and treatment
While overexposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke and ultraviolet radiation is widely recognized as a significant risk factor for cancer, it’s essential to acknowledge that the overconsumption of unnecessary medications also play a substantial role in cancer development. Medications can cause damage to genes through various mechanisms, including direct DNA damage, interference with DNA repair mechanisms, and disruption of cellular signaling pathways. This can lead to mutations and alterations in gene expression patterns, ultimately increasing the risk of cancer development.
Maintaining a balanced diet, a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise are vital components of a healthy lifestyle that can help reduce the risk of cancer and other diseases. However, despite these healthy practices, genetic factors can still predispose individuals to cancer. Nonetheless, advancements in homeopathy offer treatments and solutions for various diseases, including cancer. It’s important to acknowledge that we’re at a point where the notion of incurability must be discarded, and faith in medical science, particularly in homeopathy, needs to be reinstated. It’s time to recognize the innate capacities of the human body and its remarkable ability to heal.